A protocol for looking critically at content and developing a sensitivity to the role(s) of power and participation in the design of objects and systems.

A protocol for looking critically at content and developing a sensitivity to the role(s) of power and participation in the design of objects and systems.

This routine encourages students to consider the diverse perspectives that different people within a particular system may have based on their role in the system. This routine fosters perspective taking and can help children generate new questions and/or ideas about the system, how it works, and how it might be improved.

This tool is connected to the Agency by Design Making Moves. The Making Moves identifies three maker capacities that support a sensitivity to design, along with their associated learning moves. Here you’ll find three observation sheets, one for each of the maker capacities: Looking Closely, Exploring Complexity, and Finding Opportunity.

The Agency by Design guide to implementing maker-centered teaching and learning
Maker-Centered Learning provides both a theoretical framework and practical resources for the educators, curriculum developers, librarians, administrators, and parents navigating this burgeoning field. Written by the expert team from the Agency by Design initiative at Harvard's Project Zero, this book
A surge of voices from government, industry, and education have argued that, in order to equip the next generation for life and work in the decades ahead, it is vital to support maker-centered learning in various educational environments. Maker-Centered Learning provides insight into what that means, and offers tools and knowledge that can be applied anywhere that learning takes place.
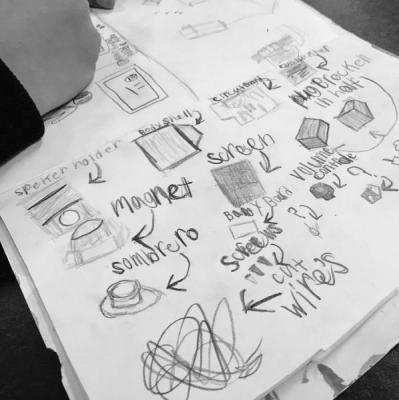
This practice allows learners to notice features of an object that they may not have the vocabulary to fully describe yet. By doing several sketches, learners have the chance to engage in perspective taking and to see details they might miss at first glance.

Students from King Middle School in Portland, Maine, explain the importance of looking closely in a maker-centered classroom.
Video by Alex Coppola
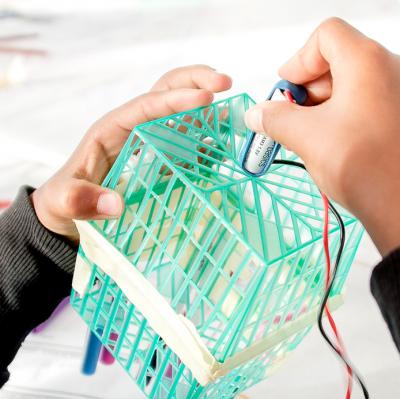
Agency by Designer project Director Shari Tishman introduces the concept of “maker empowerment” as a potential outcome of maker learning experiences.

This thinking routine helps learners to think in the past, present, and future, viewing their making in the context of a long-term and broad trajectory of learning. It is meant to cultivate an ongoing reflective practice in the classroom.

A practice that promotes the capacity of looking closely is the Elaboration Game. This picture of practice essay shares a version that was adapted by educator Tatum Omari for a group of young learners to examine a tortilla press during their unit of study about bread making.